Hanoi: Recording outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease at preschools
Cumulatively from the beginning of 2023 until now, Hanoi has recorded 2,063 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease, an increase of nearly 1.4 times compared to the same period in 2022, but no deaths have been recorded.
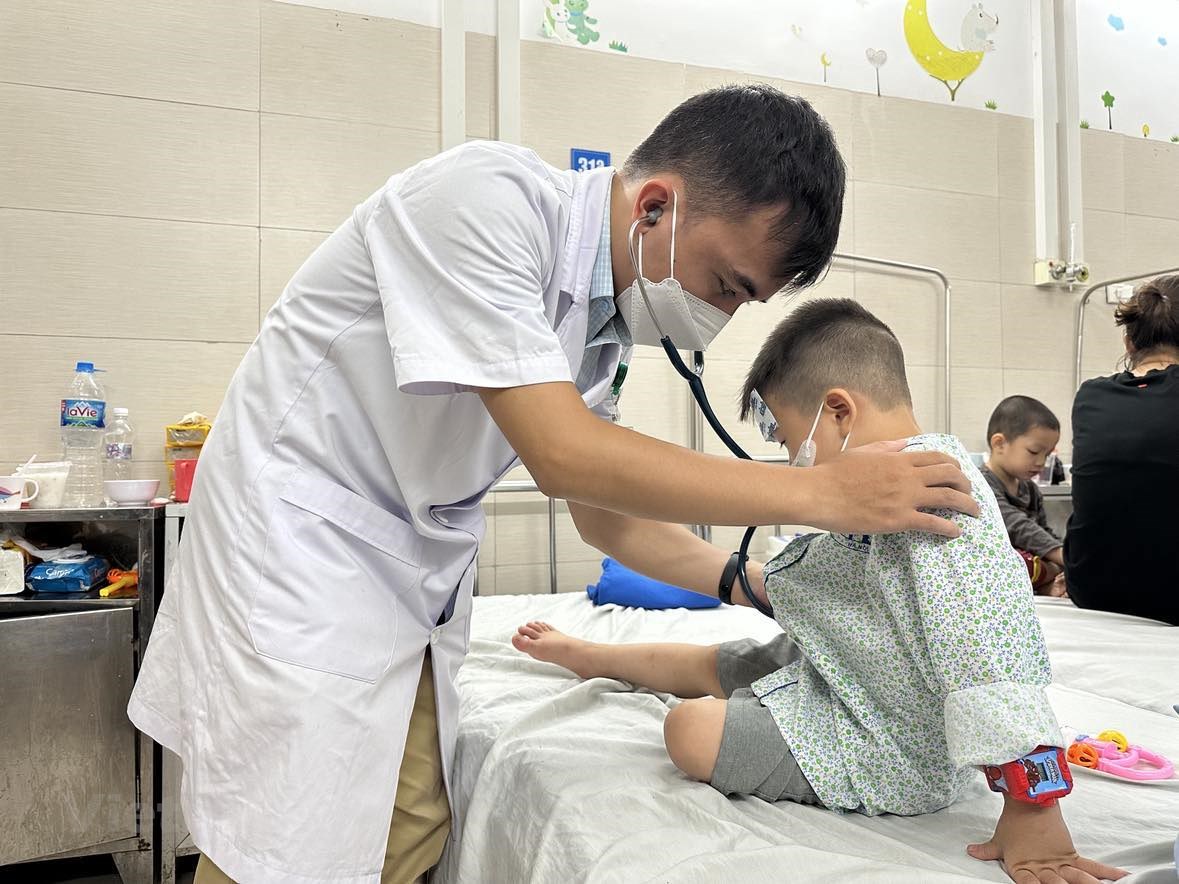
According to information from the Hanoi Center for Disease Control (CDC), during the week (from September 29 to October 6), Hanoi had 265 more cases of hand, foot and mouth disease (nearly doubling compared to the previous week). ).
Some districts in Hanoi City recorded many patients with hand, foot and mouth disease such as: Soc Son (69 cases), Cau Giay (26 cases), Hoai Duc (25 cases), Ha Dong (18 cases), Ba Vi (15 cases), Thanh Xuan (15 cases), Dong Da (12 cases).
[Ca Mau: Two children died from dengue fever and hand, foot and mouth disease]
Thus, the number of cases of hand, foot and mouth disease in the first week of October doubled compared to the last 2 weeks of September and increased more than 3.5 times compared to the end of August.
Specifically, at the end of August and early September 2023, on average each week, the city recorded 70-75 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease. By the last 2 weeks of September, the number of cases increased to about 140 cases/week.
Cumulatively from the beginning of 2023 until now, Hanoi has recorded 2,063 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease (an increase of nearly 1.4 times compared to the same period in 2022) but no deaths have been recorded.
In addition, during the week (from September 29 to October 6), the city also recorded 2 more outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease in 2 districts: Soc Son and Dong Da. Cumulatively from the beginning of the year until now, there have been 47 outbreaks, currently 2 outbreaks are still active.
According to the Hanoi CDC's assessment, changing seasons, erratic rain and sunshine combined with students returning to school after summer break cause the number of hand, foot and mouth cases to increase. In particular, in the past week, some districts with a high number of cases such as Soc Son, Cau Giay, Hoai Duc... have recorded outbreaks in preschools and kindergartens. It is predicted that in the coming weeks, patients may continue to increase.
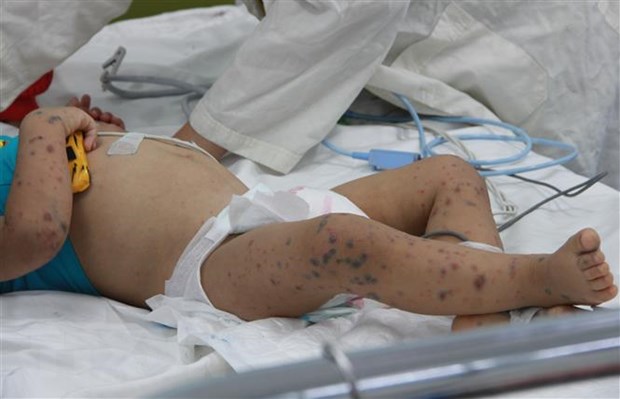
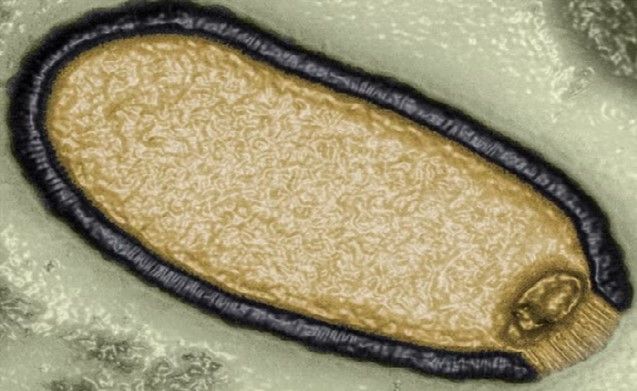
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an infectious disease caused by the Enterovirus group of intestinal viruses, most commonly Coxsackie A16 and Enterovirus type 71. Among them, Enterovirus type 71 (EV71) causes many dangerous complications of encephalitis, meningitis, pneumonia, myocarditis and can lead to death. The disease can occur at any age, but up to 90% occurs in young children, especially children under 5 years old.
Hanoi CDC recommends that to prevent and control hand, foot and mouth disease in preschools and elementary schools, it is necessary to increase cleaning of classrooms, toys, students' towels... and at the same time instruct teachers on how to Measures to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease.
There is currently no vaccine to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease and no specific treatment. Disease prevention measures include personal hygiene and environmental sanitation to limit spread.
Parents should not be subjective when their children have hand, foot and mouth disease and need to closely monitor the progression of the disease.
To prevent, people and communities need to proactively follow the instructions of the Ministry of Health as follows:
- Wash your hands regularly with soap under running water several times a day (both adults and children), especially before preparing food, before eating/feeding children, before holding children, and after eating. go to the toilet, after changing diapers and cleaning the child.
- Practice good food hygiene: eat well, drink well; Eating utensils must be washed thoroughly before use (preferably soaked in boiling water); ensure the use of clean water in daily activities; Do not feed the child food; Do not let children eat with their hands, suck hands, or suck on toys; Do not let children share napkins, handkerchiefs, or eating utensils such as cups, bowls, plates, spoons, or unsterilized toys.
- Regularly clean daily contact surfaces and tools such as toys, learning tools, door handles, stair handrails, table/chair surfaces, and floors with soap or regular detergents. .
- Do not let children come into contact with people who are sick or suspected of being sick.
- Use a hygienic latrine. The patient's feces and other waste must be collected and dumped into a hygienic latrine.
- When detecting signs of suspected illness in a child, take the child for examination or immediately notify the nearest medical agency./.







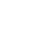

 Facebook
Facebook
 Tweet
Tweet
 Zalo
Zalo





 News
News















 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google