Be careful in the prevention of Marburg - a highly fatal disease
The Ministry of Health suggested localities to strengthen surveillance of the particularly dangerous Marburg disease, which is classified in group A in the Law on Prevention of Infectious Diseases of our country. can be as high as 88%). Note those who enter from countries with epidemics in Africa within 21 days

Recently, Deputy Minister of Health Nguyen Thi Lien Huong signed a document to the People's Committees of provinces and cities across the country and the Institutes of Hygiene and Epidemiology / Pasteur Institute on strengthening supervision of Marburg disease prevention.
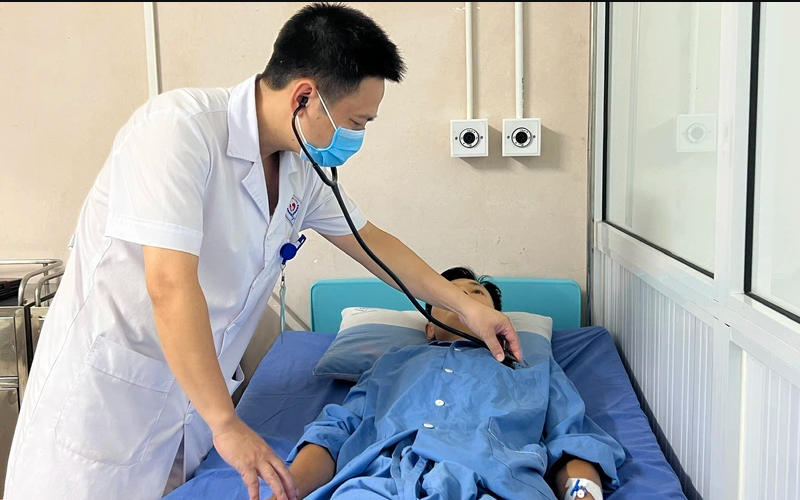
Accordingly, Marburg disease is an acute infectious disease caused by Marburg virus. This is a particularly dangerous disease, with high transmissibility and mortality rate (up to 88%).
The Ministry of Health suggested that the People's Committees of provinces and cities across the country, the Institutes of Hygiene and Epidemiology, and Pasteur actively strengthen supervision of Marburg disease prevention and control to prevent the disease from spreading into Vietnam. Requesting the People's Committees of provinces and cities to direct the Department of Health to strengthen close monitoring of people on entry, in the community and at medical facilities to early detect suspected cases for epidemiological investigation, note people entering from countries with epidemics in the African region within 21 days; In collaboration with the Institutes of Hygiene and Epidemiology, Pasteur took samples for diagnostic testing, case management (if any) and prevented the disease from spreading to the community.
In addition, fully implement personal protective measures for medical staff and people in contact with suspected/infected cases, so as not to infect health workers as well as spread in the community. copper…
Marburg is transmitted from person to person through direct contact (through broken skin or mucous membranes) with blood, bodily fluids (urine, sweat, saliva, vomit, breast milk, etc.), and with surfaces surfaces and materials (eg, bedding, clothing) contaminated with these fluids.
The incubation period varies from two to 21 days; onset with symptoms of high fever, headache, malaise, then may appear diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, vomiting, bleeding. The illness caused by the Marburg virus begins suddenly with a high fever, severe headache, and severe malaise. Severe diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, and nausea and vomiting may begin on the third day. Severe hemorrhagic manifestations appear five to seven days after symptom onset, and deaths often involve some form of bleeding, often from multiple sites. In fatal cases, death most commonly occurs between 8 and 9 days after symptom onset, often preceded by severe blood loss and shock.
Although there is no approved vaccine or antiviral treatment to treat the virus, supportive care — rehydration with oral or intravenous fluids — and treatment of specific symptoms help improve survivability. A variety of potential treatments are being evaluated, including blood products, immunotherapy, and drug therapy.








 Facebook
Facebook
 Tweet
Tweet
 Zalo
Zalo






 News
News















 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google