Marburg disease prevention and control: Surveillance at border gates and borders
- In order to detect early cases of marburg disease, promptly handle the disease to prevent its spread, and minimize morbidity and mortality, the Binh Phuoc Health sector is proactively implementing prevention and control plans. pandemic.
According to the plan to prevent and control the marburg epidemic, which has just been issued by the Binh Phuoc Department of Health, the unit gave three situations: the disease has not been recorded, the occurrence of invasive diseases and the disease spreading rapidly in the community. Localities, health agencies and relevant units should strengthen coordination in disease surveillance in the community. Medical units monitor, detect early, be ready to collect and treat patients; strengthen propaganda on the epidemic situation and prevention and control measures to the people; take samples for testing and report, send samples to Pasteur Institute in Ho Chi Minh City for diagnosis and identification of the disease.
The Health sector has drastically implemented surveillance activities in the community in order to detect people at risk early to isolate and prevent the epidemic from entering and spreading on a large scale; Close medical supervision for people coming and going from epidemic areas, people at risk and symptoms suspected of having the disease. Hospitals organize classification, collection, emergency treatment, patient treatment, sampling and testing to promptly detect suspected cases; fully prepare disinfectant chemicals, supplies, equipment and human resources to be ready to support and deploy anti-epidemic activities in a timely manner.
The provincial Center for Disease Control monitors the number of tourists passing through border gates bordering Cambodia into Binh Phuoc. The Center collaborates with units of the Culture, Sports and Tourism sectors to enhance information on tourists, especially those coming from African epidemic areas, to communicate and encourage them to self-monitor their health. , promptly report to health authorities if there are symptoms of suspected marburg disease. The center cooperates with medical facilities to isolate and manage visitors when detecting suspected cases.
The Provincial Center for Disease Control cooperates with units of the Labor - Invalids and Social Affairs sectors to monitor the health situation of workers who are working or departing from or returning from areas where there is a shortage of workers. African translation; did not organize to send Binh Phuoc workers to epidemic areas.
Local authorities in the province mobilize people to voluntarily declare to health authorities if there is an epidemiological factor going back and forth from an epidemic area; at the same time detect people with symptoms of fever, diarrhea, hemorrhage, and have epidemiological risk factors for marburg disease to be isolated, diagnosed and treated promptly; People are advised not to go to epidemic areas.
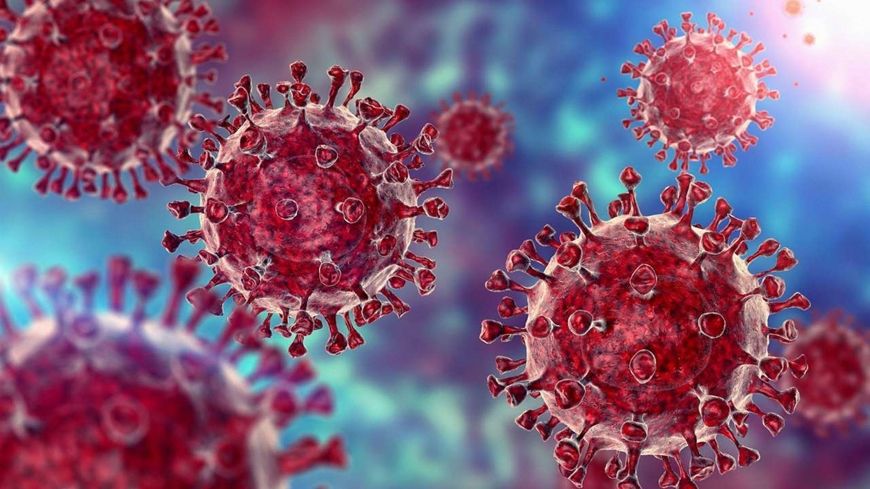
According to the Ministry of Health, marburg is a particularly dangerous acute infectious disease, with a mortality rate of up to 88%. The disease is caused by the marburg virus. The natural reservoir is fruit bats. The disease can be transmitted from animals to humans, from person to person through direct contact with blood, body fluids (urine, sweat, saliva, vomit, breast milk, semen ...), or with the lips. Schools, objects contaminated by secretions of people infected with the Marburg virus. The incubation period is from 2 to 21 days, with the onset of symptoms of high fever, headache, malaise, then diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, vomiting, bleeding may appear. There is no vaccine or specific treatment for marburg disease. The disease is classified in group A in the Law on Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases of Vietnam.
Binh Phuoc is managing 4 border gates, including: Hoa Lu international border gate; main border gate Hoang Dieu, Loc Thinh; Tan Tien sub-border gate and an opening. The province shares a 260 km border with Cambodia. Binh Phuoc Border Guard and related units are organizing dozens of checkpoints and checkpoints along the border to ensure security and safety as well as prevent and control epidemics.








 Facebook
Facebook
 Tweet
Tweet
 Zalo
Zalo





 News
News















 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google